Low-sodium diets have been gaining in popularity in recent years as people become more health conscious. A low-sodium diet involves eating foods that have low sodium (in other words, salt) content.
This diet can offer various health benefits, including lower blood pressure and a reduced risk of heart disease.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider before starting a low-sodium diet.
In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of a low-sodium diet and provide guidelines for how to manage one successfully!
What Is A Low-Sodium Diet?
A low-sodium diet is a diet that includes foods that are low in sodium. Sodium is a mineral that is found in salt. It is also found in some foods, such as processed meats and cheeses.
A low-sodium diet can help to prevent or treat high blood pressure. It can also help to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
There are many different ways to follow a low-sodium diet. One way is to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables. Fresh fruits and vegetables are naturally low in sodium. Another way is to cook at home more often.
When you cook at home, you can control the amount of salt that you use. You can also look for low-sodium versions of your favorite foods.
If you have high blood pressure or if you are at risk for heart disease, stroke, or kidney disease, talk to your doctor about whether a low-sodium diet is right for you.
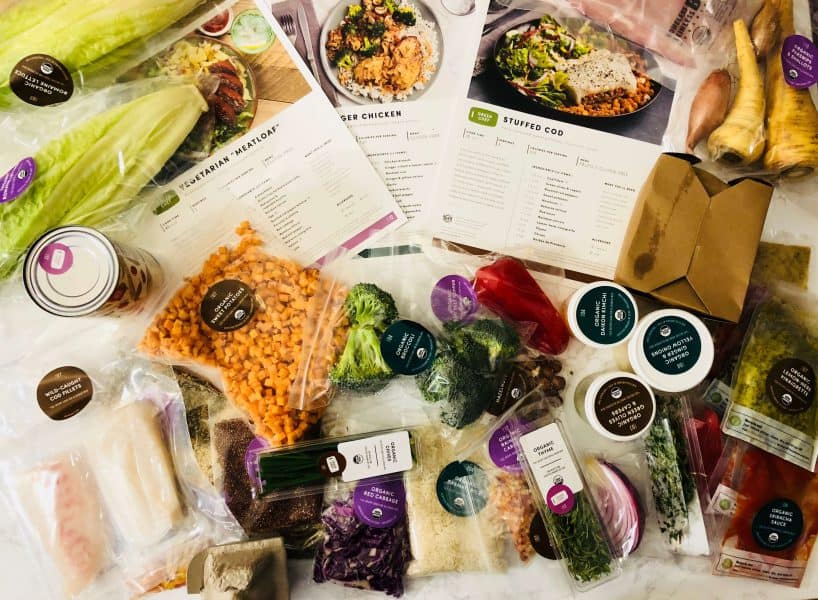
Check out the best low-sodium meal delivery kits>>
Benefits Of Low-Sodium Diet
When it comes to dieting, one of the most important things to consider is how much sodium you’re consuming.
Sodium is a key component in many processed foods and can have negative effects on your health if you consume too much of it. A low-sodium diet has numerous benefits that can help improve your overall health.

Lower Your Blood Pressure.
One of the primary benefits of a low-sodium diet is that it can help to lower your blood pressure.
This is because sodium can cause your body to retain water, which in turn increases blood volume and leads to higher blood pressure.
If you have high blood pressure or are at risk of developing it, reducing your sodium intake can help to prevent or control the condition.
When you consume less sodium, your blood pressure is reduced. This can be extremely beneficial for those who suffer from hypertension, or high blood pressure. A low-sodium diet can also help to prevent hypertension from developing in the first place.
Reduce Your Risk Of Heart Disease.
When you reduce your sodium intake, you can also help to lower your blood pressure. This, in turn, reduces your risk of developing heart disease.
While a high sodium diet is a major contributor to high blood pressure, other factors contribute as well. These include being overweight, having diabetes, and smoking.
So even if you have a family history of heart disease, you can help to reduce your risk by eating a low-sodium diet.
Reduce Water Retention And Bloating
One of the benefits of a low-sodium diet is that it can help to reduce water retention.
When you consume too much salt, your body holds on to water to dilute the high concentration of sodium in your blood.
This can lead to bloating and swelling, especially in the hands, feet, and ankles. Reducing your sodium intake can help to reduce water retention and improve your overall health.
Improve Kidney Function
The benefits of a low-sodium diet are not only limited to heart health. Studies have shown that reducing sodium intake can also improve kidney function.
This is especially beneficial for people with renal problems or hypertension. In one study, participants who reduced their sodium intake by 34% had a significant improvement in kidney function.
The results were even more pronounced in people with hypertension. Thus, a low-sodium diet is not only good for your heart but also your kidneys.
Check out the best low-sodium meal delivery kits>>
Disadvantages Of Low-Sodium Diet
If you are considering a low-sodium diet, there are a few things you should be aware of. While there are some benefits to this type of diet, there are also some potential disadvantages.
One of the biggest disadvantages is that it can be difficult to stick to. That is where meal kits or meal delivery plans can help you a lot! When you get an organized meal planning designed for your needs, it makes it much easier to stick to the diet for the short and long run. See our recommended low-sodium diet meal kits here
When you eliminate or significantly reduce sodium in your diet, you may find that you are missing some of your favorite foods. You may also have to cook more meals at home since many processed and restaurant foods are high in sodium.
Another downside is that a low-sodium diet can sometimes cause fatigue and headaches.
This is because sodium helps to regulate fluid levels in the body. When you reduce sodium, you may also need to increase your intake of other electrolytes, such as potassium and magnesium.
Lastly, a low-sodium diet may not be suitable for everyone. If you have certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or high blood pressure, you should speak to your doctor before making any changes to your diet.
How To Manage Low-Sodium Diet?
If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, or kidney disease, your doctor may have advised you to follow a low-sodium diet.
A low-sodium diet limits the amount of sodium (salt) you eat each day. This can be a challenge since sodium is found in many foods, even some that don’t taste salty.
Here are some tips to help you manage a low-sodium diet:
- Read food labels carefully. Look for foods that are labeled “low sodium,” “reduced sodium,” or “no salt added.”
- Choose fresh or frozen fruits and vegetables more often than canned. When buying canned fruits and vegetables, look for ones packed in water with no salt added.
- Limit processed meats such as bacon, lunchmeat, and hot dogs. Choose leaner cuts of meat and poultry. Trim away any visible fat before cooking.
- Avoid using salty seasoning mixes, bouillon cubes, and soy sauce. Instead, flavor your food with herbs, spices, lemon, lime, or vinegar.
- Use less salt when cooking. Try not to add salt when eating. Get in the habit of tasting your food before adding salt. You may find that you don’t need it.
Conclusion
A low-sodium diet has many potential benefits, including reducing water retention, improving kidney function, and lowering blood pressure.
However, it is not suitable for everyone and can be difficult to stick to. If you are considering a low-sodium diet, speak to your doctor first to help you determine if this type of diet is suitable for you or not.